nf-core/viralrecon
Assembly and intrahost/low-frequency variant calling for viral samples
2.0). The latest
stable release is
2.6.0
.
Introduction
This document describes the output produced by the pipeline. Most of the plots are taken from the MultiQC report, which summarises results at the end of the pipeline.
The directories listed below will be created in the results directory after the pipeline has finished. All paths are relative to the top-level results directory.
Nanopore: Pipeline overview
- Preprocessing
- pycoQC - Sequencing QC
- artic guppyplex - Aggregate pre-demultiplexed reads from MinKNOW/Guppy
- NanoPlot - Read QC
- Variant calling
- artic minion - Align reads, call variants and generate consensus sequence
- Downstream analysis
- SAMtools - Remove unmapped reads and obtain alignment metrics
- mosdepth - Genome-wide and amplicon coverage QC plots
- BCFTools - Variant count metrics
- SnpEff and SnpSift - Genetic variant annotation and functional effect prediction
- QUAST - Consensus assessment report
- Pangolin - Lineage analysis
- Nextclade - Clade assignment, mutation calling and sequence quality checks
- ASCIIGenome - Individual variant screenshots with annotation tracks
- Workflow reporting
- MultiQC - Present QC, visualisation and custom reporting for sequencing, raw reads, alignment and variant calling results
Nanopore: Preprocessing
A file called summary_variants_metrics_mqc.csv containing a selection of read alignment and variant calling metrics will be saved in the multiqc/<CALLER>/ output directory which is determined by the --artic_minion_caller parameter (Default: nanopolish/). The same metrics will also be added to the top of the MultiQC report.
Nanopore: pycoQC
Output files
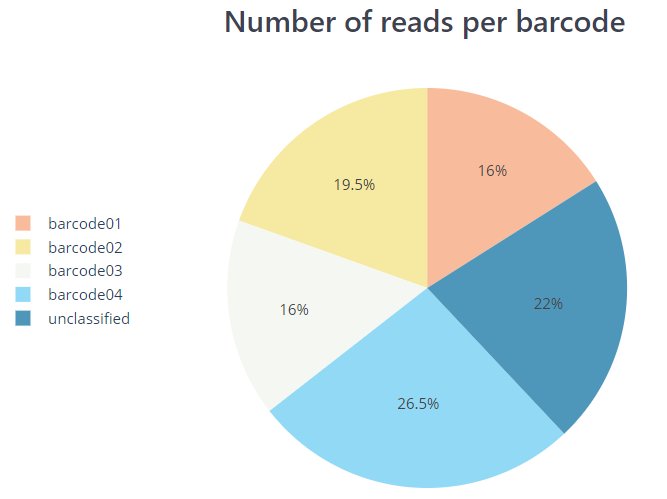
pycoqc/*.htmland.jsonfile that includes a run summary and graphical representation of various QC metrics including distribution of read length, distribution of read quality scores, mean read quality per sequence length, output per channel over experiment time and percentage of reads per barcode.
PycoQC compute metrics and generate QC plots using the sequencing summary information generated by basecalling/demultiplexing tools such as Guppy e.g. distribution of read length, read length over time, number of reads per barcode and other general stats.
Nanopore: artic guppyplex
Output files
guppyplex/*.fastq.gzfiles generated by aggregate pre-demultiplexed reads from MinKNOW/Guppy. These files are not saved by default but can be via a custom config file such as the one below.
params {
modules {
'nanopore_artic_guppyplex' {
publish_files = ['fastq.gz':'']
}
}
}The artic guppyplex tool from the ARTIC field bioinformatics pipeline is used to perform length filtering of the demultiplexed Nanopore reads obtained per barcode. This essentially filters out chimeric reads that may be generated by the ARTIC protocol. The pipeline uses a default minimum and maximum read length of 400 and 700, respectively as tailored for the nCoV-2019 primer set. However, you may need to adjust these for different primer schemes e.g. by using the minimum length of the amplicons (--min-length) as well as the maximum length plus 200 (--max-length).
Nanopore: NanoPlot
Output files
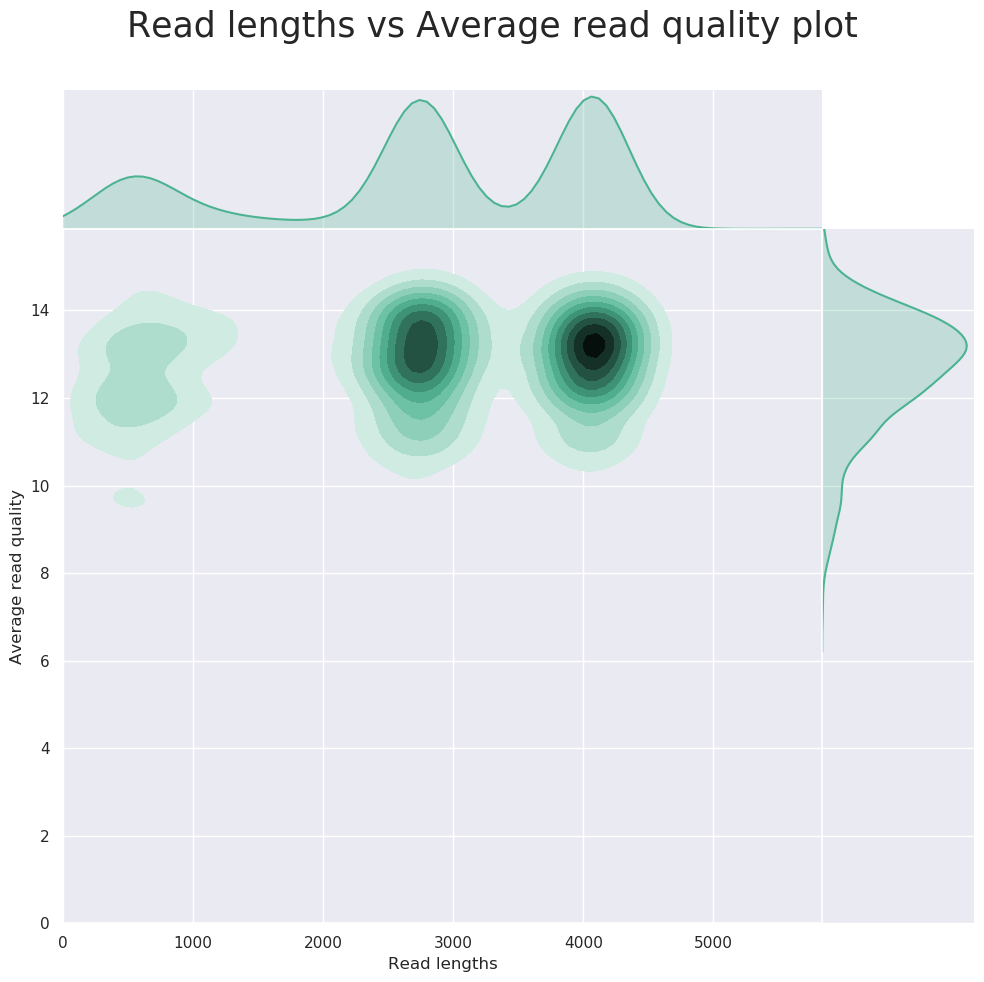
nanoplot/<SAMPLE>/- Per-sample
*.htmlfiles for QC metrics and individual*.pngimage files for plots.
- Per-sample
NanoPlot it a tool that can be used to produce general quality metrics from various Nanopore-based input files including fastq files e.g. quality score distribution, read lengths and other general stats.
Nanopore: Variant calling
Nanopore: artic minion
Output files
<CALLER>/*.consensus.fasta: Consensus fasta file generated by artic minion.*.pass.vcf.gz: VCF file containing variants passing quality filters.*.pass.vcf.gz.tbi: VCF index file containing variants passing quality filters.*.primers.vcf: VCF file containing variants found in primer-binding regions.*.merged.vcf: VCF file containing all detected variants.*.fail.vcf: VCF file containing variants failing quality filters.*.sorted.bam: BAM file generated by initial alignment.*.sorted.bam.bai: BAM index file generated by initial alignment.*.trimmed.rg.sorted.bam: BAM file without primer-binding site trimming.*.trimmed.rg.sorted.bam.bai: BAM index file without primer-binding site trimming.*.primertrimmed.rg.sorted.bam: BAM file generated after primer-binding site trimming.*.primertrimmed.rg.sorted.bam.bai: BAM index file generated after primer-binding site trimming.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --artic_minion_caller parameter (Default: ‘nanopolish’).
The artic minion tool from the ARTIC field bioinformatics pipeline is used to align reads, call variants and to generate the consensus sequence. By default, artic minion uses Minimap2 to align the reads to the viral genome, however you can use BWA instead using the --artic_minion_aligner bwa parameter. Similarly, the default variant caller used by artic minion is Nanopolish, however, you can use Medaka instead via the --artic_minion_caller medaka parameter. Medaka is faster than Nanopolish, performs mostly the same and can be run directly from fastq input files as opposed to requiring the fastq, fast5 and sequencing_summary.txt files required to run Nanopolish. You must provide the appropriate Medaka model via the --artic_minion_medaka_model parameter if using --artic_minion_caller medaka.
Nanopore: Downstream analysis
Nanopore: SAMtools
Output files
<CALLER>/*.mapped.sorted.bam: Coordinate sorted BAM file containing read alignment information.*.mapped.sorted.bam.bai: Index file for coordinate sorted BAM file.
<CALLER>/samtools_stats/- SAMtools
*.mapped.sorted.bam.flagstat,*.mapped.sorted.bam.idxstatsand*.mapped.sorted.bam.statsfiles generated from the alignment files.
- SAMtools
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --artic_minion_caller parameter (Default: ‘nanopolish’).
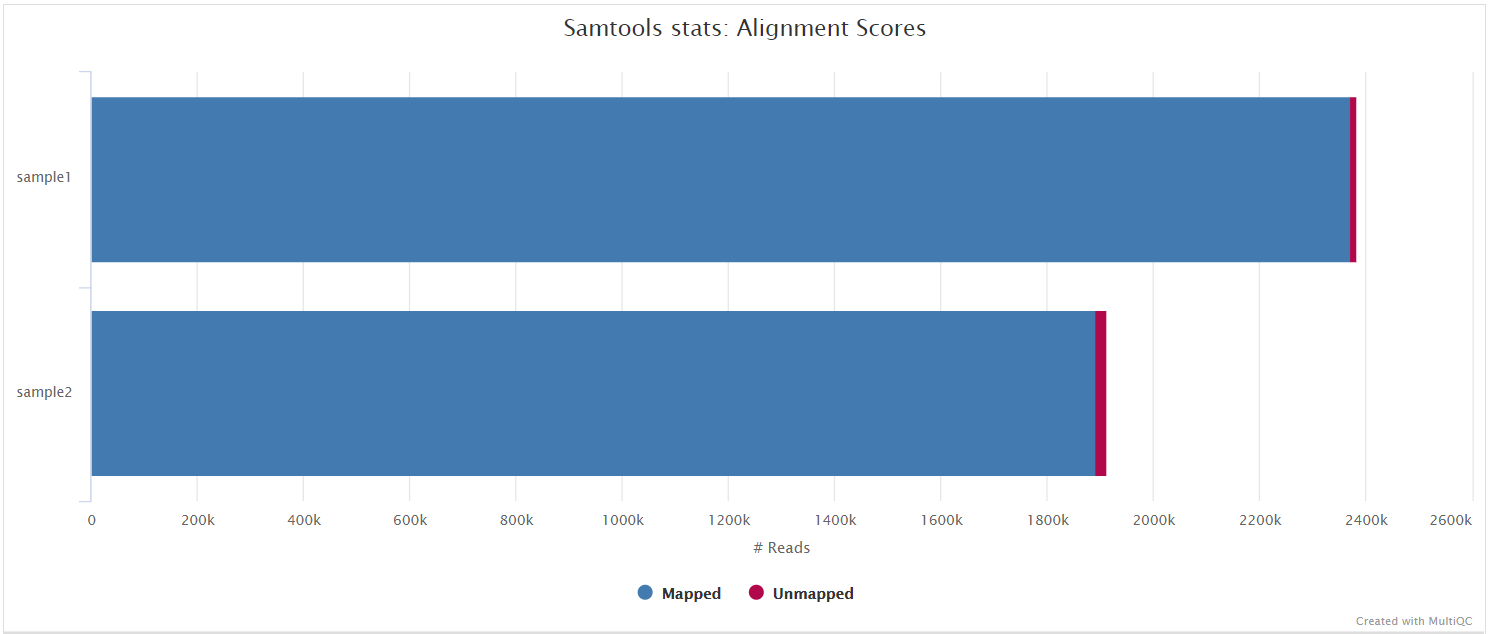
BAM files containing the original alignments from either Minimap2 or BWA are further processed with SAMtools to remove unmapped reads as well as to generate read mapping statistics.
Nanopore: mosdepth
Output files
<CALLER>/mosdepth/genome/all_samples.mosdepth.coverage.tsv: File aggregating genome-wide coverage values across all samples used for plotting.*.mosdepth.coverage.pdf: Whole-genome coverage plot.*.mosdepth.coverage.tsv: File containing coverage values for the above plot.*.mosdepth.summary.txt: Summary metrics including mean, min and max coverage values.
<CALLER>/mosdepth/amplicon/all_samples.mosdepth.coverage.tsv: File aggregating per-amplicon coverage values across all samples used for plotting.all_samples.mosdepth.heatmap.pdf: Heatmap showing per-amplicon coverage across all samples.*.mosdepth.coverage.pdf: Bar plot showing per-amplicon coverage for an individual sample.*.mosdepth.coverage.tsv: File containing per-amplicon coverage values for the above plot.*.mosdepth.summary.txt: Summary metrics including mean, min and max coverage values.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --artic_minion_caller parameter (Default: ‘nanopolish’).
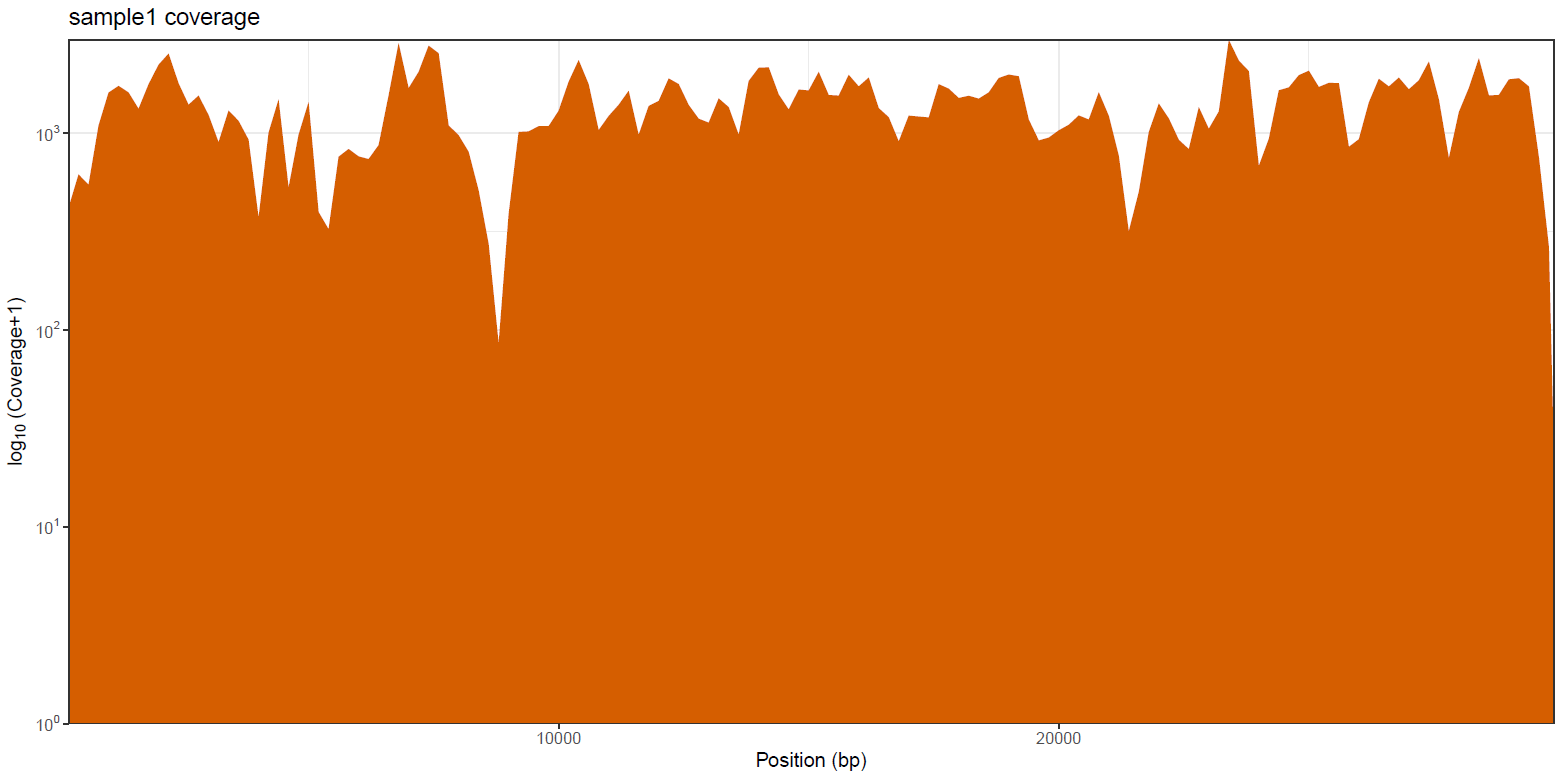
mosdepth is a fast BAM/CRAM depth calculation for WGS, exome, or targeted sequencing. mosdepth is used in this pipeline to obtain genome-wide coverage values in 200bp windows and to obtain amplicon/region-specific coverage metrics. The results are then either rendered in MultiQC (genome-wide coverage) or are plotted using custom R scripts.
![]()
![]()
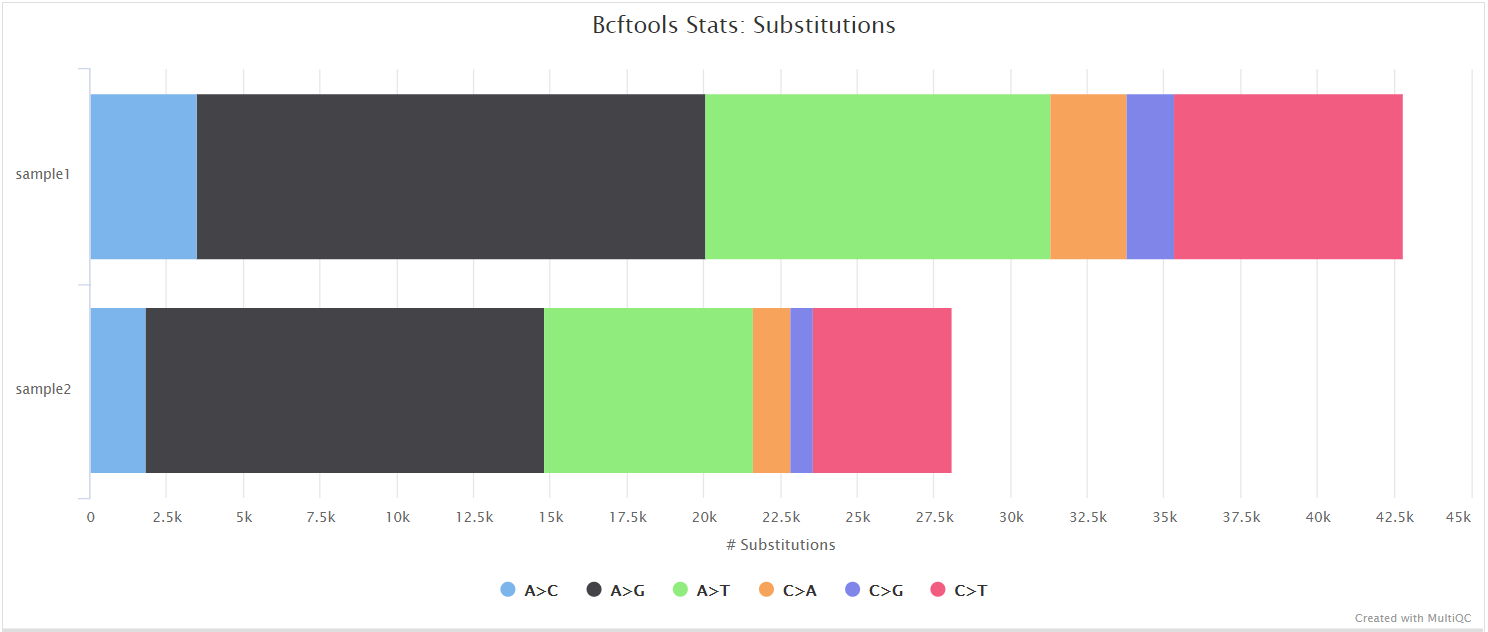
Nanopore: BCFTools
Output files
<CALLER>/bcftools_stats/*.bcftools_stats.txt: Statistics and counts obtained from VCF file.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --artic_minion_caller parameter (Default: ‘nanopolish’).
BCFtools is a set of utilities that manipulate variant calls in VCF and its binary counterpart BCF format. It can also used be used to generate statistics and counts obtained from VCF files as used here.
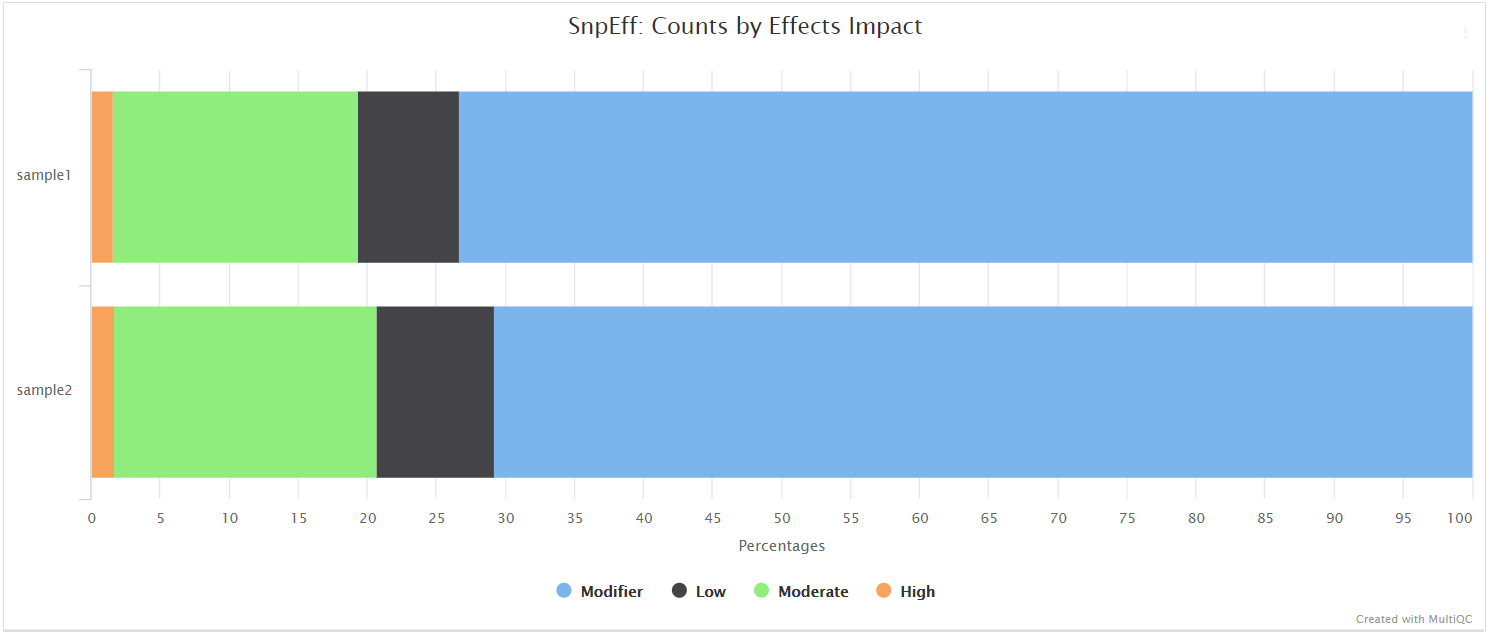
Nanopore: SnpEff and SnpSift
Output files
<CALLER>/snpeff/*.snpeff.csv: Variant annotation csv file.*.snpeff.genes.txt: Gene table for annotated variants.*.snpeff.summary.html: Summary html file for variants.*.snpeff.vcf.gz: VCF file with variant annotations.*.snpeff.vcf.gz.tbi: Index for VCF file with variant annotations.*.snpsift.txt: SnpSift summary table.
<CALLER>/snpeff/bcftools_stats/*.snpeff.bcftools_stats.txt: Statistics and counts obtained from SnpEff VCF file.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --artic_minion_caller parameter (Default: ‘nanopolish’).
SnpEff is a genetic variant annotation and functional effect prediction toolbox. It annotates and predicts the effects of genetic variants on genes and proteins (such as amino acid changes).
SnpSift annotates genomic variants using databases, filters, and manipulates genomic annotated variants. After annotation with SnpEff, you can use SnpSift to help filter large genomic datasets in order to find the most significant variants.
Nanopore: QUAST
Output files
<CALLER>/quast/report.html: Results report in HTML format. Also available in various other file formats i.e.report.pdf,report.tex,report.tsvandreport.txt.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --artic_minion_caller parameter (Default: ‘nanopolish’).
QUAST is used to generate a single report with which to evaluate the quality of the consensus sequence across all of the samples provided to the pipeline. The HTML results can be opened within any browser (we recommend using Google Chrome). Please see the QUAST output docs for more detailed information regarding the output files.
Nanopore: Pangolin
Output files
<CALLER>/pangolin/*.pangolin.csv: Lineage analysis results from Pangolin.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --artic_minion_caller parameter (Default: ‘nanopolish’).
Phylogenetic Assignment of Named Global Outbreak LINeages (Pangolin) has been used extensively during the COVID-19 pandemic to assign lineages to SARS-CoV-2 genome sequenced samples. A web application also exists that allows users to upload genome sequences via a web browser to assign lineages to genome sequences of SARS-CoV-2, view descriptive characteristics of the assigned lineage(s), view the placement of the lineage in a phylogeny of global samples, and view the temporal and geographic distribution of the assigned lineage(s).
Nanopore: Nextclade
Output files
<CALLER>/nextclade/*.csv: Analysis results from Nextlade containing genome clade assignment, mutation calling and sequence quality checks.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --artic_minion_caller parameter (Default: ‘nanopolish’).
Nextclade performs viral genome clade assignment, mutation calling and sequence quality checks for the consensus sequences generated in this pipeline. Similar to Pangolin, it has been used extensively during the COVID-19 pandemic. A web application also exists that allows users to upload genome sequences via a web browser.
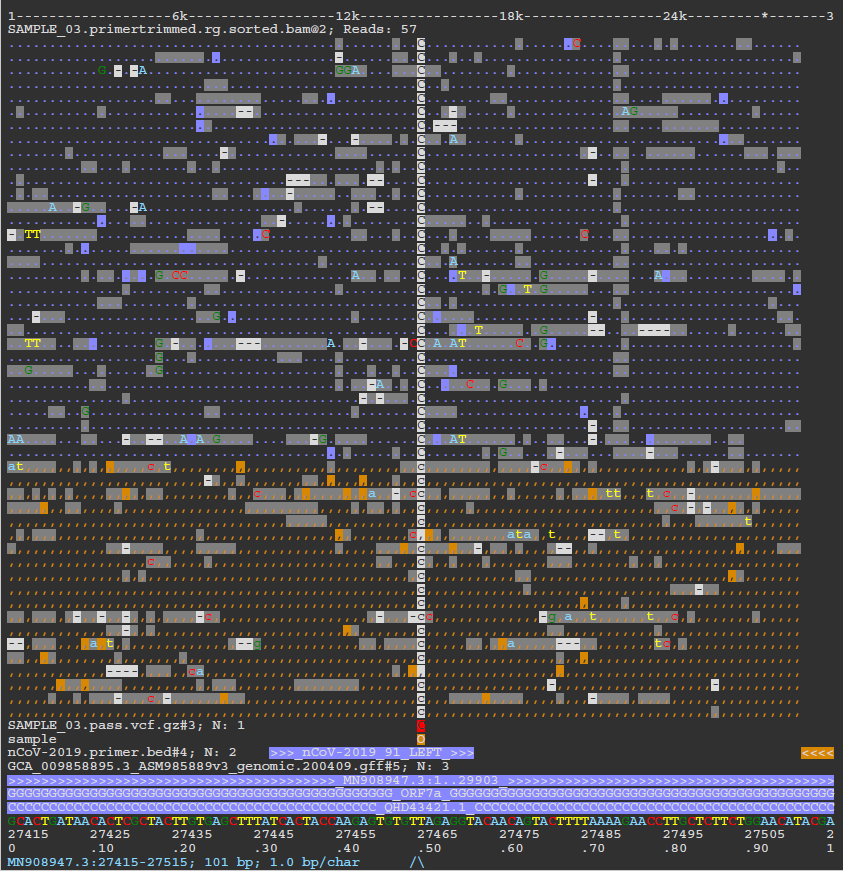
Nanopore: ASCIIGenome
Output files
<CALLER>/asciigenome/<SAMPLE>/*.pdf: Individual variant screenshots with annotation tracks in PDF format.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --artic_minion_caller parameter (Default: ‘nanopolish’).
As described in the documentation, ASCIIGenome is a command-line genome browser that can be run from a terminal window and is solely based on ASCII characters. The closest program to ASCIIGenome is probably samtools tview but ASCIIGenome offers much more flexibility, similar to popular GUI viewers like the IGV browser. We are using the batch processing mode of ASCIIGenome in this pipeline to generate individual screenshots for all of the variant sites reported for each sample in the VCF files. This is incredibly useful to be able to quickly QC the variants called by the pipeline without having to tediously load all of the relevant tracks into a conventional genome browser. Where possible, the BAM read alignments, VCF variant file, primer BED file and GFF annotation track will be represented in the screenshot for contextual purposes. The screenshot below shows a SNP called relative to the MN908947.3 SARS-CoV-2 reference genome that overlaps the ORF7a protein and the nCoV-2019_91_LEFT primer from the ARIC v3 protocol.
Nanopore: Workflow reporting
Nanopore: MultiQC
Output files
multiqc/<CALLER>/multiqc_report.html: a standalone HTML file that can be viewed in your web browser.multiqc_data/: directory containing parsed statistics from the different tools used in the pipeline.summary_variants_metrics_mqc.csv: file containing a selection of read alignmnet and variant calling metrics. The same metrics will also be added to the top of the MultiQC report.
MultiQC is a visualization tool that generates a single HTML report summarizing all samples in your project. Most of the pipeline QC results are visualised in the report and further statistics are available in the report data directory.
Results generated by MultiQC collate pipeline QC from pycoQC, samtools, mosdepth, BCFTools, SnpEff and QUAST.
The default multiqc config file has been written in a way in which to structure these QC metrics to make them more interpretable in the final report.
The pipeline has special steps which also allow the software versions to be reported in the MultiQC output for future traceability. For more information about how to use MultiQC reports, see http://multiqc.info.
An example MultiQC report generated from a full-sized dataset can be viewed on the nf-core website.
Illumina: Pipeline overview
- Preprocessing
- Variant calling
- Bowtie 2 - Read alignment relative to reference genome
- SAMtools - Sort, index and generate metrics for alignments
- iVar trim - Primer sequence removal for amplicon data
- picard MarkDuplicates - Duplicate read marking and removal
- picard CollectMultipleMetrics - Alignment metrics
- mosdepth - Whole-genome and amplicon coverage metrics
- iVar variants and iVar consensus || BCFTools and BEDTools - Variant calling and consensus sequence generation
- SnpEff and SnpSift - Genetic variant annotation and functional effect prediction
- QUAST - Consensus assessment report
- Pangolin - Lineage analysis
- Nextclade - Clade assignment, mutation calling and sequence quality checks
- ASCIIGenome - Individual variant screenshots with annotation tracks
- BCFTools isec - Intersect variants across all callers
- De novo assembly
- Workflow reporting and genomes
- MultiQC - Present QC for raw reads, alignment, assembly and variant calling
- Reference genome files - Save reference genome indices/files
Illumina: Preprocessing
cat
Output files
fastq/*.merged.fastq.gz: These files are not saved by default but can be via a custom config file such as the one below.
params {
modules {
'illumina_cat_fastq' {
publish_files = null
}
}
}If multiple libraries/runs have been provided for the same sample in the input samplesheet (e.g. to increase sequencing depth) then these will be merged at the very beginning of the pipeline in order to have consistent sample naming throughout the pipeline. Please refer to the usage documentation to see how to specify these samples in the input samplesheet.
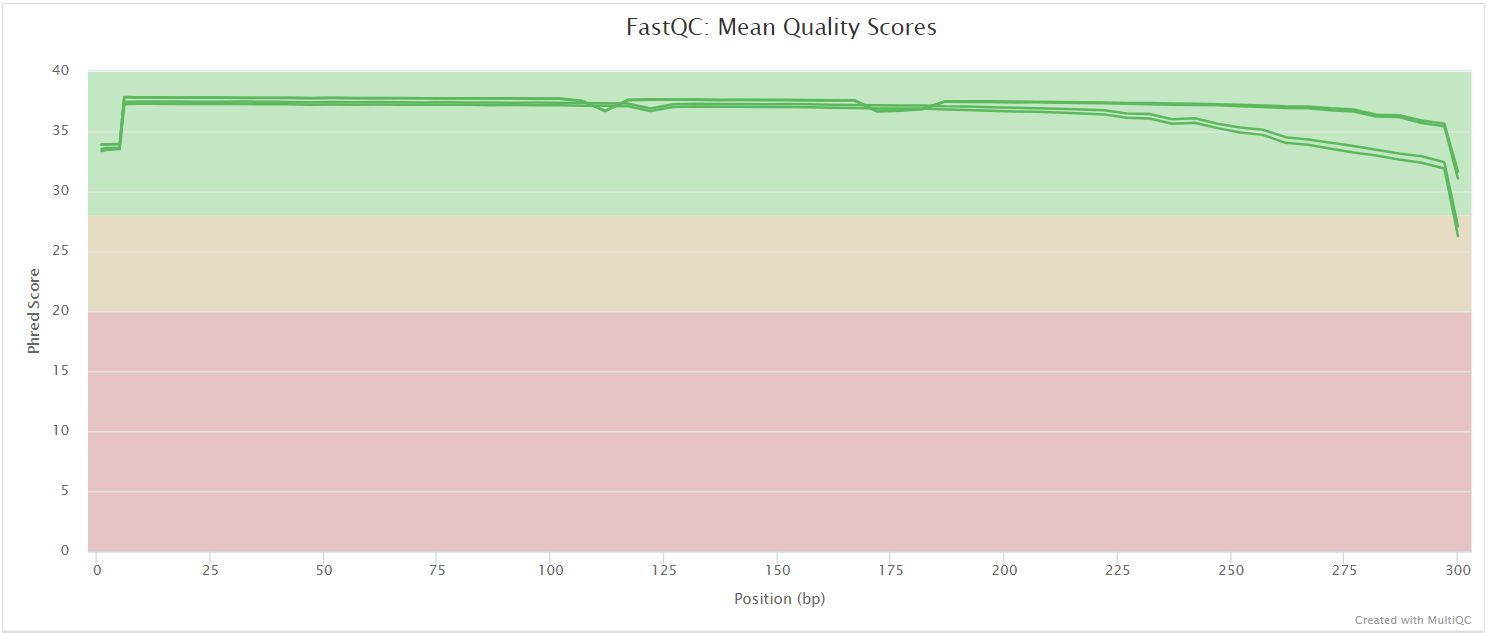
FastQC
Output files
fastqc/raw/*_fastqc.html: FastQC report containing quality metrics.*_fastqc.zip: Zip archive containing the FastQC report, tab-delimited data file and plot images.
NB: The FastQC plots in this directory are generated relative to the raw, input reads. They may contain adapter sequence and regions of low quality. To see how your reads look after trimming please refer to the FastQC reports in the fastqc/trim/ directory.
FastQC gives general quality metrics about your sequenced reads. It provides information about the quality score distribution across your reads, per base sequence content (%A/T/G/C), adapter contamination and overrepresented sequences. For further reading and documentation see the FastQC help pages.
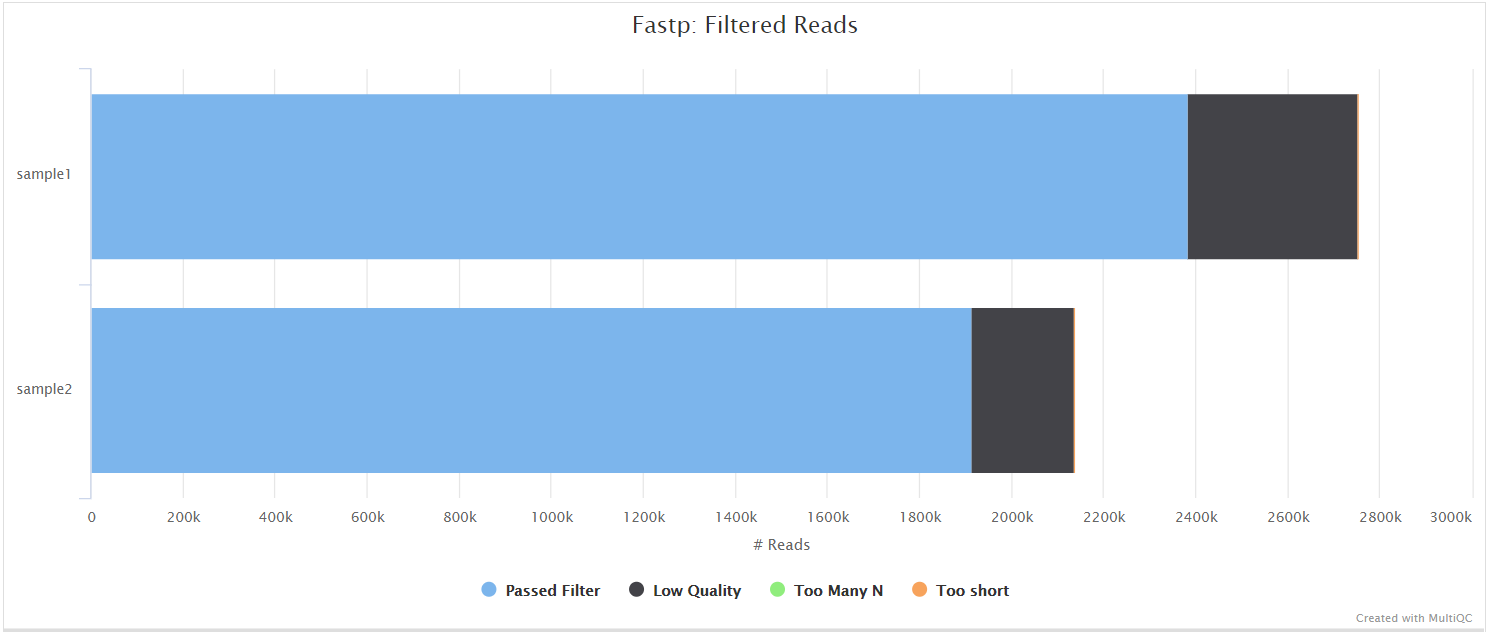
fastp
Output files
fastp/*.fastp.html: Trimming report in html format.*.fastp.json: Trimming report in json format.
fastp/log/*.fastp.log: Trimming log file.
fastqc/trim/*_fastqc.html: FastQC report of the trimmed reads.*_fastqc.zip: Zip archive containing the FastQC report, tab-delimited data file and plot images.
fastp is a tool designed to provide fast, all-in-one preprocessing for FastQ files. It has been developed in C++ with multithreading support to achieve higher performance. fastp is used in this pipeline for standard adapter trimming and quality filtering.
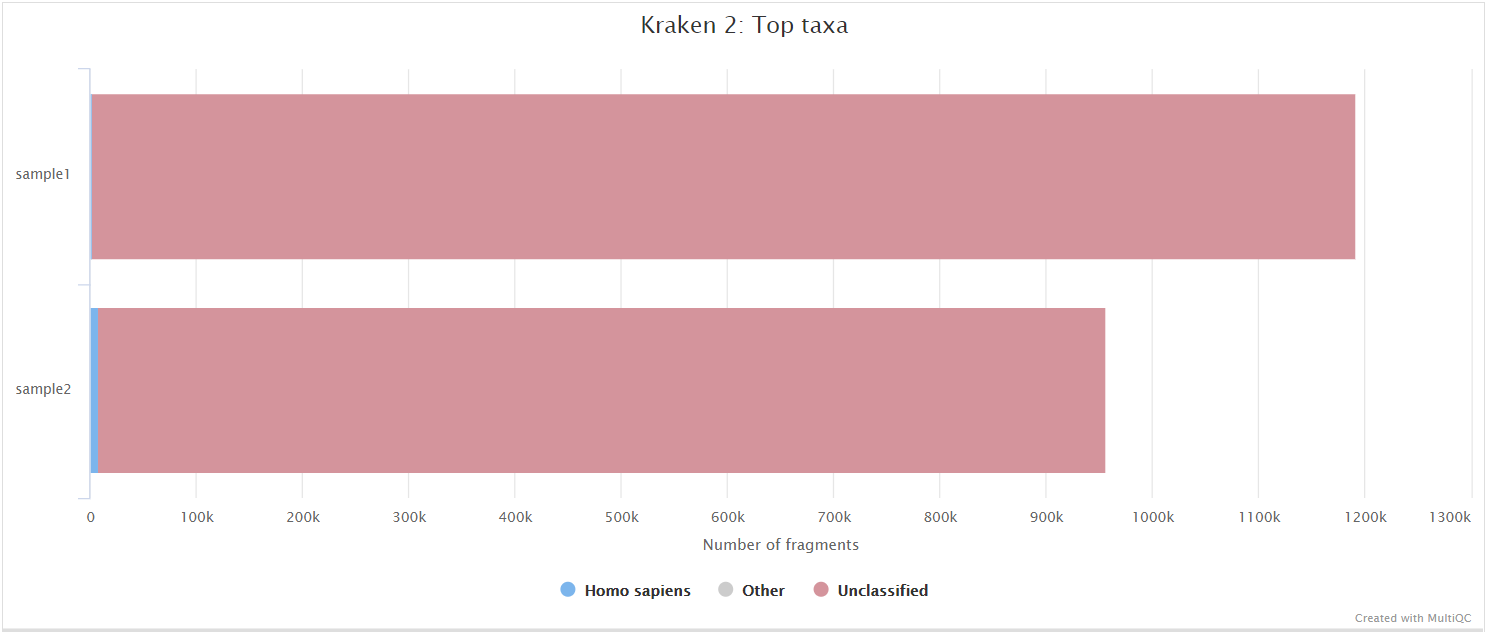
Kraken 2
Output files
kraken2/*.kraken2.report.txt: Kraken 2 taxonomic report. See here for a detailed description of the format.
Kraken 2 is a sequence classifier that assigns taxonomic labels to DNA sequences. Kraken 2 examines the k-mers within a query sequence and uses the information within those k-mers to query a database. That database maps k-mers to the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of all genomes known to contain a given k-mer.
We use a Kraken 2 database in this workflow to filter out reads specific to the host genome before performing the de novo assembly steps in the pipeline. This filtering is not performed in the variant calling arm of the pipeline by default but Kraken 2 is still run to obtain an estimate of host reads, however, the filtering can be amended via the --kraken2_variants_host_filter parameter.
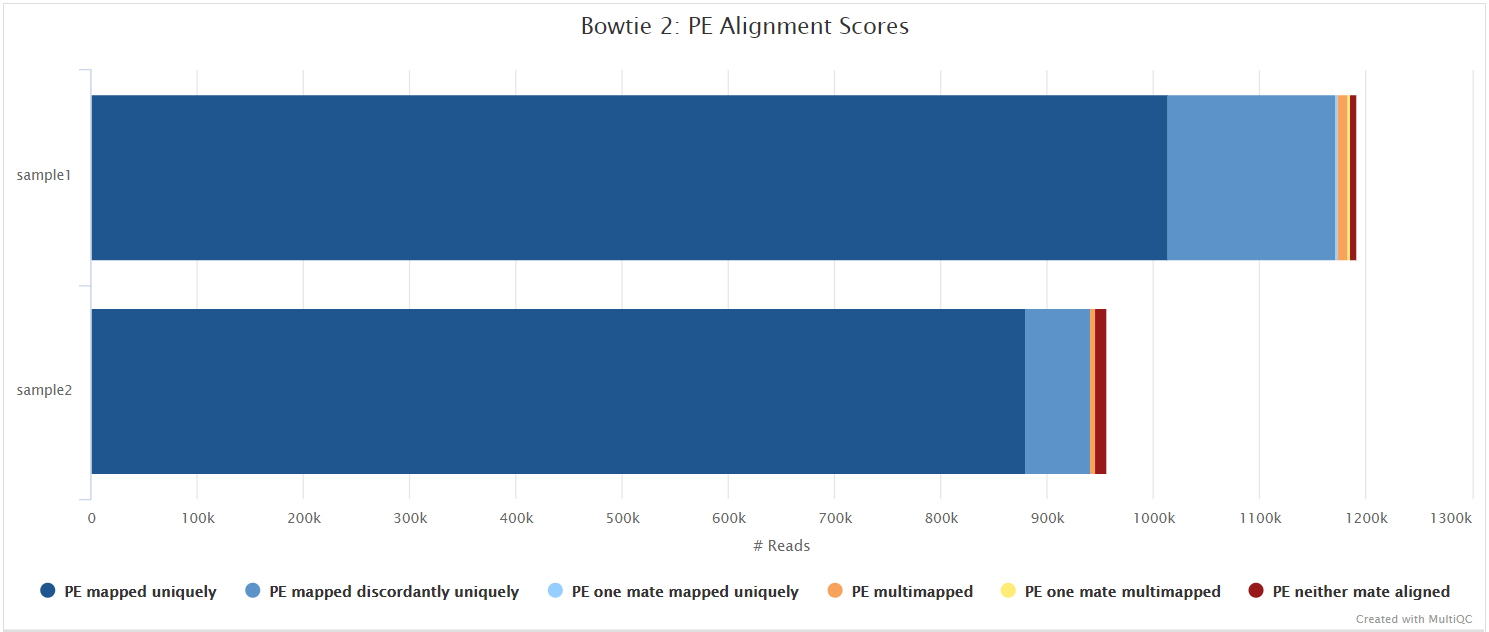
Illumina: Variant calling
A file called summary_variants_metrics_mqc.csv containing a selection of read alignment and variant calling metrics will be saved in the multiqc/ results directory. The same metrics will also be added to the top of the MultiQC report.
Bowtie 2
Output files
variants/bowtie2/log/*.bowtie2.log: Bowtie 2 mapping log file.
Bowtie 2 is an ultrafast and memory-efficient tool for aligning sequencing reads to long reference sequences. Bowtie 2 supports gapped, local, and paired-end alignment modes.
SAMtools
Output files
variants/bowtie2/<SAMPLE>.sorted.bam: Coordinate sorted BAM file containing read alignment information.<SAMPLE>.sorted.bam.bai: Index file for coordinate sorted BAM file.
variants/bowtie2/samtools_stats/- SAMtools
<SAMPLE>.sorted.bam.flagstat,<SAMPLE>.sorted.bam.idxstatsand<SAMPLE>.sorted.bam.statsfiles generated from the alignment files.
- SAMtools
Bowtie 2 BAM files are further processed with SAMtools to sort them by coordinate, for indexing, as well as to generate read mapping statistics.

iVar trim
Output files
variants/bowtie2/*.ivar_trim.sorted.bam: Coordinate sorted BAM file after primer trimming.*.ivar_trim.sorted.bam.bai: Index file for coordinate sorted BAM file after primer trimming.
variants/bowtie2/samtools_stats/- SAMtools
*.ivar_trim.sorted.bam.flagstat,*.ivar_trim.sorted.bam.idxstatsand*.ivar_trim.sorted.bam.statsfiles generated from the primer trimmed alignment files.
- SAMtools
variants/bowtie2/log/*.ivar_trim.ivar.log: iVar trim log file obtained from stdout.
If the --protocol amplicon parameter is provided then iVar is used to trim amplicon primer sequences from the aligned reads. iVar uses the primer positions supplied in --primer_bed to soft clip primer sequences from a coordinate sorted BAM file.
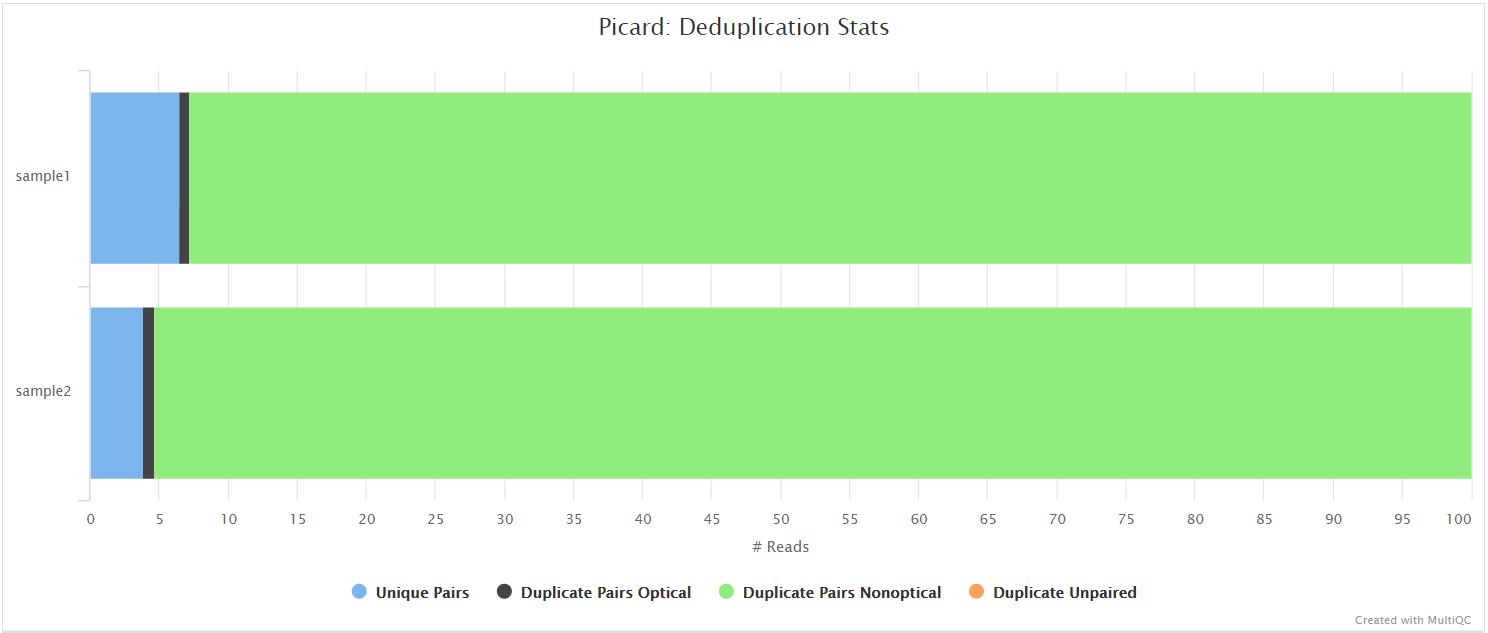
picard MarkDuplicates
Output files
variants/bowtie2/*.markduplicates.sorted.bam: Coordinate sorted BAM file after duplicate marking.*.markduplicates.sorted.bam.bai: Index file for coordinate sorted BAM file after duplicate marking.
variants/bowtie2/samtools_stats/- SAMtools
*.markduplicates.sorted.bam.flagstat,*.markduplicates.sorted.bam.idxstatsand*.markduplicates.sorted.bam.statsfiles generated from the duplicate marked alignment files.
- SAMtools
variants/bowtie2/picard_metrics/*.markduplicates.sorted.MarkDuplicates.metrics.txt: Metrics file from MarkDuplicates.
Unless you are using UMIs it is not possible to establish whether the fragments you have sequenced from your sample were derived via true biological duplication (i.e. sequencing independent template fragments) or as a result of PCR biases introduced during the library preparation. picard MarkDuplicates isn’t run by default because you anticipate high levels of duplication with viral data due to the size of the genome, however, you can activate it by adding --skip_markduplicates false to the command you use to run the pipeline. This will only mark the duplicate reads identified amongst the alignments to allow you to guage the overall level of duplication in your samples. You can also choose to remove any reads identified as duplicates via the --filter_duplicates parameter.
picard CollectMultipleMetrics
Output files
variants/bowtie2/picard_metrics/*.CollectMultipleMetrics.*: Alignment QC files from picard CollectMultipleMetrics in*_metricstextual format.
variants/bowtie2/picard_metrics/pdf/*.pdfplots for metrics obtained from CollectMultipleMetrics.
picard-tools is a set of command-line tools for manipulating high-throughput sequencing data. We use picard-tools in this pipeline to obtain mapping and coverage metrics.
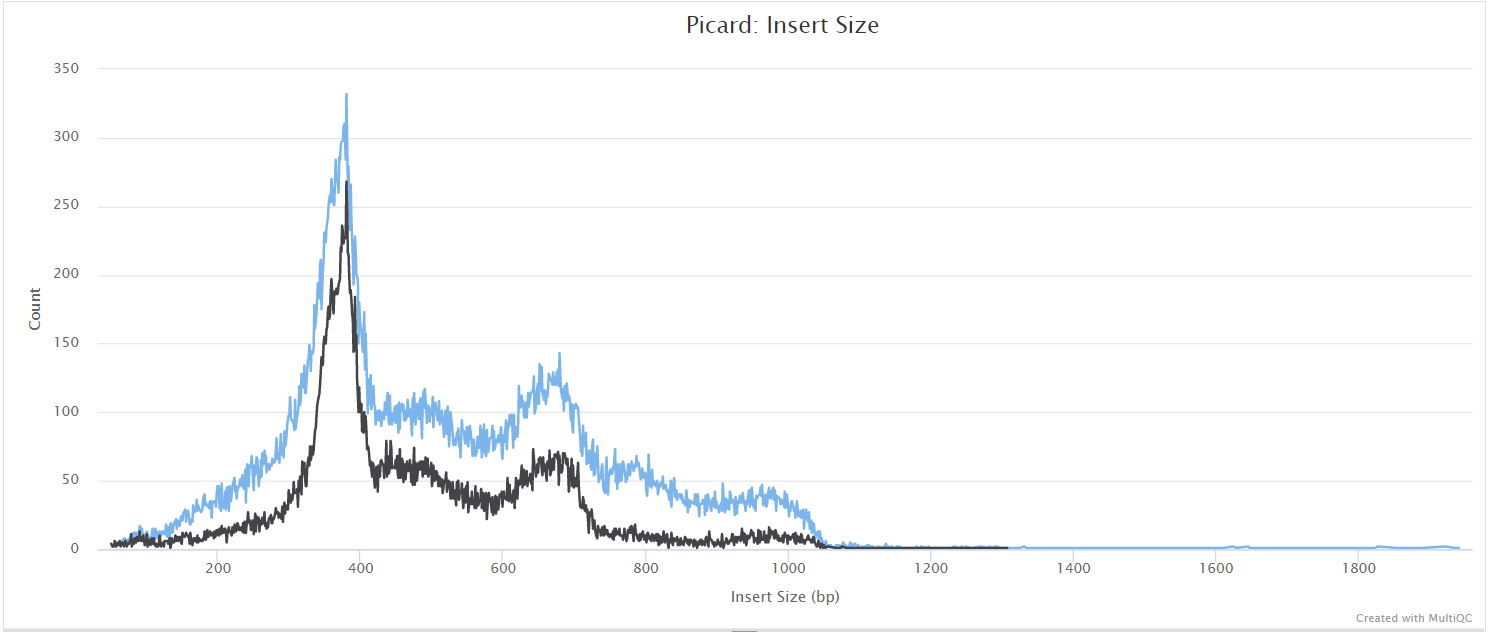
mosdepth
Output files
variants/bowtie2/mosdepth/genome/all_samples.mosdepth.coverage.tsv: File aggregating genome-wide coverage values across all samples used for plotting.*.mosdepth.coverage.pdf: Whole-genome coverage plot.*.mosdepth.coverage.tsv: File containing coverage values for the above plot.*.mosdepth.summary.txt: Summary metrics including mean, min and max coverage values.
variants/bowtie2/mosdepth/amplicon/all_samples.mosdepth.coverage.tsv: File aggregating per-amplicon coverage values across all samples used for plotting.all_samples.mosdepth.heatmap.pdf: Heatmap showing per-amplicon coverage across all samples.*.mosdepth.coverage.pdf: Bar plot showing per-amplicon coverage for an individual sample.*.mosdepth.coverage.tsv: File containing per-amplicon coverage values for the above plot.*.mosdepth.summary.txt: Summary metrics including mean, min and max coverage values.
mosdepth is a fast BAM/CRAM depth calculation for WGS, exome, or targeted sequencing. mosdepth is used in this pipeline to obtain genome-wide coverage values in 200bp windows and for --protocol amplicon to obtain amplicon/region-specific coverage metrics. The results are then either rendered in MultiQC (genome-wide coverage) or are plotted using custom R scripts.
![]()

![]()
iVar variants and iVar consensus
Output files
variants/ivar/*.tsv: Original iVar variants in TSV format.*.vcf.gz: iVar variants in VCF format.*.vcf.gz.tbi: iVar variants in VCF index file.
variants/ivar/consensus/*.consensus.fa: Consensus Fasta file generated by iVar.*.consensus.qual.txt: File with the average quality of each base in the consensus sequence.
variants/ivar/consensus/base_qc/*.ACTG_density.pdf: Plot showing density of ACGT bases within the consensus sequence.*.base_counts.pdf: Plot showing frequency and percentages of all bases in consensus sequence.*.base_counts.tsv: File containing frequency and percentages of all bases in consensus sequence.*.N_density.pdf: Plot showing density of N bases within the consensus sequence.*.N_run.tsv: File containing start positions and width of N bases in consensus sequence.
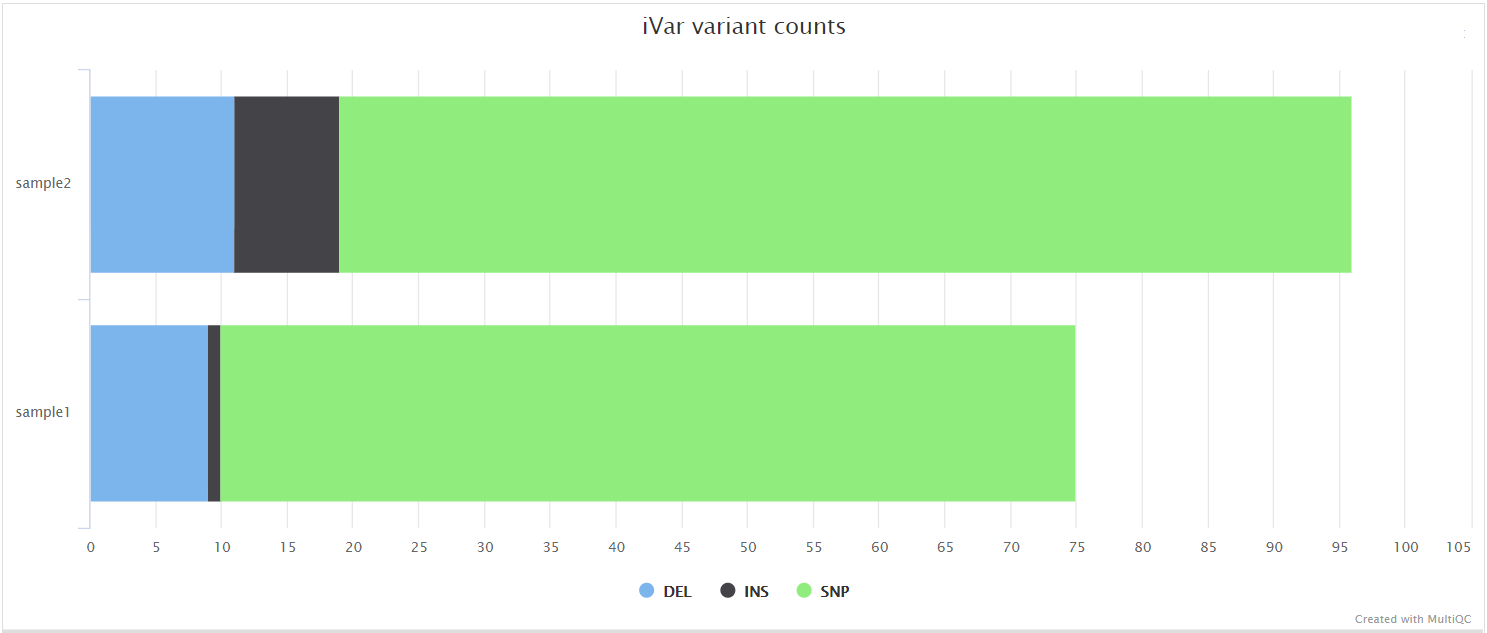
variants/ivar/log/*.variant_counts.log: Counts for type of variants called by iVar.
variants/ivar/bcftools_stats/*.bcftools_stats.txt: Statistics and counts obtained from iVar variants VCF file.
iVar is a computational package that contains functions broadly useful for viral amplicon-based sequencing. We use iVar in this pipeline to trim primer sequences for amplicon input data as well as to call variants and for consensus sequence generation.
BCFTools and BEDTools
Output files
variants/bcftools/*.vcf.gz: Variants VCF file.*.vcf.gz.tbi: Variants VCF index file.
variants/bcftools/consensus/*.consensus.fa: Consensus Fasta file generated by integrating the variants called by BCFTools into the reference genome.
variants/bcftools/consensus/base_qc/*.ACTG_density.pdf: Plot showing density of ACGT bases within the consensus sequence.*.base_counts.pdf: Plot showing frequency and percentages of all bases in consensus sequence.*.base_counts.tsv: File containing frequency and percentages of all bases in consensus sequence.*.N_density.pdf: Plot showing density of N bases within the consensus sequence.*.N_run.tsv: File containing start positions and width of N bases in consensus sequence.
variants/bcftools/bcftools_stats/*.bcftools_stats.txt: Statistics and counts obtained from VCF file.
BCFtools can be used to call variants directly from BAM alignment files. The functionality to call variants with BCFTools in this pipeline was inspired by work carried out by Conor Walker.
BCFtools is a set of utilities that manipulate variant calls in VCF and its binary counterpart BCF format. BCFTools is used in the variant calling and de novo assembly steps of this pipeline to obtain basic statistics from the VCF output. It can also used be used to generate a consensus sequence by integrating variant calls into the reference genome.
BEDTools is a swiss-army knife of tools for a wide-range of genomics analysis tasks. In this pipeline we use bedtools genomecov to compute the per-base mapped read coverage in bedGraph format, and bedtools maskfasta to mask sequences in a Fasta file based on intervals defined in a feature file. This may be useful for creating your own masked genome file based on custom annotations or for masking all but your target regions when aligning sequence data from a targeted capture experiment.

SnpEff and SnpSift
Output files
variants/<CALLER>/snpeff/*.snpeff.csv: Variant annotation csv file.*.snpeff.genes.txt: Gene table for annotated variants.*.snpeff.summary.html: Summary html file for variants.*.snpeff.vcf.gz: VCF file with variant annotations.*.snpeff.vcf.gz.tbi: Index for VCF file with variant annotations.*.snpsift.txt: SnpSift summary table.
variants/<CALLER>/snpeff/bcftools_stats/*.bcftools_stats.txt: Statistics and counts obtained from VCF file.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --callers parameter (Default: ‘ivar’ for ‘—protocol amplicon’ and ‘bcftools’ for ‘—protocol metagenomic’).
SnpEff is a genetic variant annotation and functional effect prediction toolbox. It annotates and predicts the effects of genetic variants on genes and proteins (such as amino acid changes).
SnpSift annotates genomic variants using databases, filters, and manipulates genomic annotated variants. After annotation with SnpEff, you can use SnpSift to help filter large genomic datasets in order to find the most significant variants.

QUAST
Output files
variants/<CALLER>/quast/report.html: Results report in HTML format. Also available in various other file formats i.e.report.pdf,report.tex,report.tsvandreport.txt.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --callers parameter (Default: ‘ivar’ for ‘—protocol amplicon’ and ‘bcftools’ for ‘—protocol metagenomic’).
QUAST is used to generate a single report with which to evaluate the quality of the consensus sequence across all of the samples provided to the pipeline. The HTML results can be opened within any browser (we recommend using Google Chrome). Please see the QUAST output docs for more detailed information regarding the output files.
Pangolin
Output files
variants/<CALLER>/pangolin/*.pangolin.csv: Lineage analysis results from Pangolin.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --callers parameter (Default: ‘ivar’ for ‘—protocol amplicon’ and ‘bcftools’ for ‘—protocol metagenomic’).
Phylogenetic Assignment of Named Global Outbreak LINeages (Pangolin) has been used extensively during the COVID-19 pandemic in order to to assign lineages to SARS-CoV-2 genome sequenced samples. A web application also exists that allows users to upload genome sequences via a web browser to assign lineages to genome sequences of SARS-CoV-2, view descriptive characteristics of the assigned lineage(s), view the placement of the lineage in a phylogeny of global samples, and view the temporal and geographic distribution of the assigned lineage(s).
Nextclade
Output files
variants/<CALLER>/nextclade/*.csv: Analysis results from Nextlade containing genome clade assignment, mutation calling and sequence quality checks.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --callers parameter (Default: ‘ivar’ for ‘—protocol amplicon’ and ‘bcftools’ for ‘—protocol metagenomic’).
Nextclade performs viral genome clade assignment, mutation calling and sequence quality checks for the consensus sequences generated in this pipeline. Similar to Pangolin, it has been used extensively during the COVID-19 pandemic. A web application also exists that allows users to upload genome sequences via a web browser.
ASCIIGenome
Output files
variants/<CALLER>/asciigenome/<SAMPLE>/*.pdf: Individual variant screenshots with annotation tracks in PDF format.
NB: The value of <CALLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --callers parameter (Default: ‘ivar’ for ‘—protocol amplicon’ and ‘bcftools’ for ‘—protocol metagenomic’).
As described in the documentation, ASCIIGenome is a command-line genome browser that can be run from a terminal window and is solely based on ASCII characters. The closest program to ASCIIGenome is probably samtools tview but ASCIIGenome offers much more flexibility, similar to popular GUI viewers like the IGV browser. We are using the batch processing mode of ASCIIGenome in this pipeline to generate individual screenshots for all of the variant sites reported for each sample in the VCF files. This is incredibly useful to be able to quickly QC the variants called by the pipeline without having to tediously load all of the relevant tracks into a conventional genome browser. Where possible, the BAM read alignments, VCF variant file, primer BED file and GFF annotation track will be represented in the screenshot for contextual purposes. The screenshot below shows a SNP called relative to the MN908947.3 SARS-CoV-2 reference genome that overlaps the ORF7a protein and the nCoV-2019_91_LEFT primer from the ARIC v3 protocol.

BCFTools isec
Output files
variants/intersect/<SAMPLE>/*.vcf.gz: VCF file containing variants common to both variant callers. There will be one file for each caller - seeREADME.txtfor details.*.vcf.gz.tbi: Index for VCF file.README.txt: File containing command used and file name mappings.sites.txt: List of variants common to both variant callers in textual format. The last column indicates presence (1) or absence (0) amongst the 2 different callers.
NB: This process will only be executed when both variant callers are specified to be run i.e. --callers ivar,bcftools.
BCFTools isec can be used to intersect the variant calls generated by the 2 different callers used in the pipeline. This permits a quick assessment of how consistently a particular variant is being called using different algorithms and to prioritise the investigation of the variants.
Illumina: De novo assembly
A file called summary_assembly_metrics_mqc.csv containing a selection of read alignment and de novo assembly related metrics will be saved in the multiqc/ results directory. The same metrics will also be added to the top of the MultiQC report.
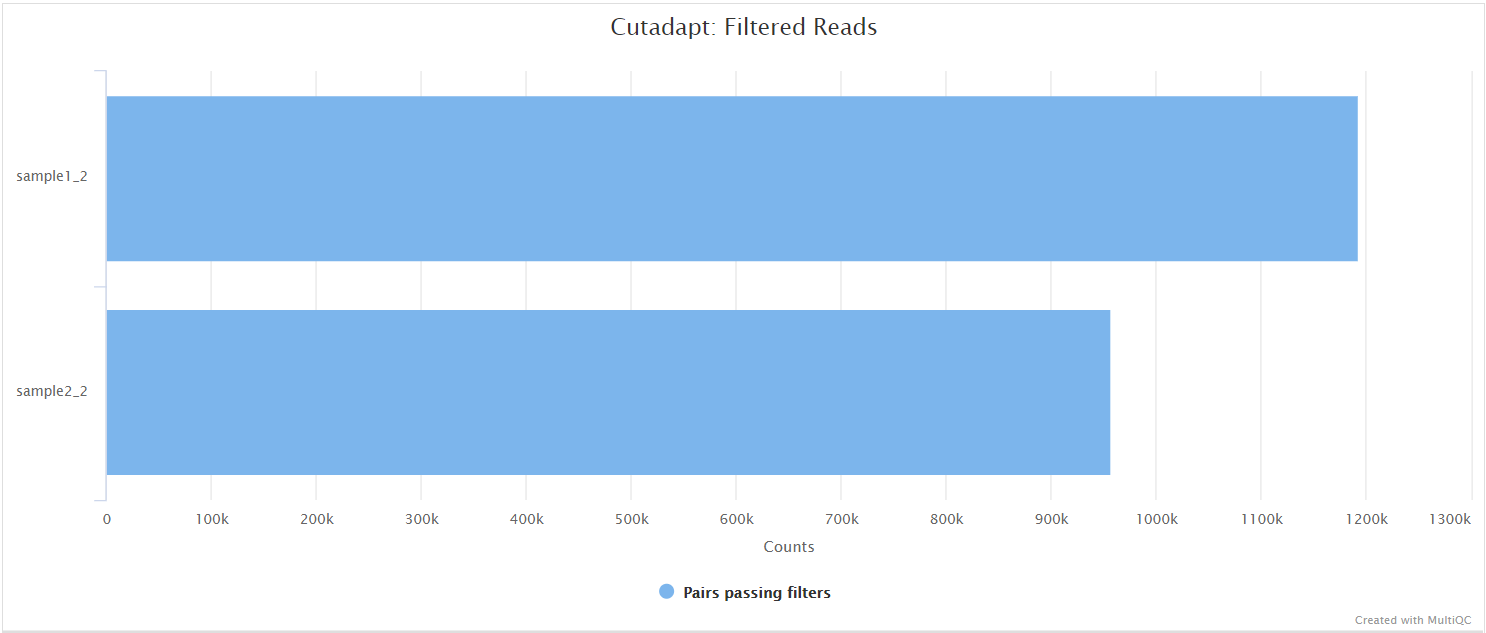
Cutadapt
Output files
assembly/cutadapt/log/*.cutadapt.log: Cutadapt log file generated from stdout.
assembly/cutadapt/fastqc/*_fastqc.html: FastQC report of the trimmed reads.*_fastqc.zip: Zip archive containing the FastQC report.
In the variant calling branch of the pipeline we are using iVar trim to remove primer sequences from the aligned BAM files for amplicon data. Since in the de novo assembly branch we don’t align the reads, we use Cutadapt as an alternative option to remove and clean the primer sequences directly from FastQ files.
SPAdes
Output files
assembly/spades/<SPADES_MODE>/*.scaffolds.fa: SPAdes scaffold assembly.*.contigs.fa: SPAdes assembly contigs.*.assembly.gfa: SPAdes assembly graph in GFA format.
assembly/spades/<SPADES_MODE>/bandage/*.png: Bandage visualisation for SPAdes assembly graph in PNG format.*.svg: Bandage visualisation for SPAdes assembly graph in SVG format.
NB: The value of <SPADES_MODE> in the output directory name above is determined by the --spades_mode parameter (Default: ‘rnaviral’).
SPAdes is an assembly toolkit containing various assembly pipelines. Generically speaking, SPAdes is one of the most popular de Bruijn graph-based assembly algorithms used for bacterial/viral genome reconstruction.
Bandage is a program for visualising de novo assembly graphs. By displaying connections which are not present in the contigs file, Bandage opens up new possibilities for analysing de novo assemblies.
Unicycler
Output files
assembly/unicycler/*.scaffolds.fa: Unicycler scaffold assembly.*.assembly.gfa: Unicycler assembly graph in GFA format.
assembly/unicycler/bandage/*.png: Bandage visualisation for Unicycler assembly graph in PNG format.*.svg: Bandage visualisation for Unicycler assembly graph in SVG format.
Unicycler is an assembly pipeline for bacterial genomes. It can assemble Illumina-only read sets where it functions as a SPAdes-optimiser.
minia
Output files
assembly/minia/*.contigs.fa: Minia scaffold assembly.*.unitigs.fa: Minia unitigs fasta file.*.h5: Minia h5 output file.
Minia is a short-read assembler based on a de Bruijn graph, capable of assembling a human genome on a desktop computer in a day. The output of Minia is a set of contigs. Minia produces results of similar contiguity and accuracy to other de Bruijn assemblers.
BLAST
Output files
assembly/<ASSEMBLER>/blastn/*.blastn.txt: BLAST results against the target virus.*.filter.blastn.txt: Filtered BLAST results.
NB: The value of <ASSEMBLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --assemblers parameter (Default: ‘spades’).
blastn is used to align the assembled contigs against the virus reference genome.
ABACAS
Output files
assembly/<ASSEMBLER>/abacas/*.abacas.bin: Bin file that contains contigs that are not used in ordering.*.abacas.crunch: Comparison file.*.abacas.fasta: Ordered and orientated sequence file.*.abacas.gaps: Gap information.*.abacas.gaps.tab: Gap information in tab-delimited format.*.abacas.MULTIFASTA.fa: A list of ordered and orientated contigs in a multi-fasta format.*.abacas.tab: Feature file*.unused_contigs.out: Information on contigs that have a mapping information but could not be used in the ordering.
assembly/<ASSEMBLER>/abacas/nucmer/: Folder containing the files generated by the NUCmer algorithm used by ABACAS.
NB: The value of <ASSEMBLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --assemblers parameter (Default: ‘spades’).
ABACAS was developed to rapidly contiguate (align, order, orientate), visualize and design primers to close gaps on shotgun assembled contigs based on a reference sequence.
PlasmidID
Output files
assembly/<ASSEMBLER>/plasmidid/<SAMPLE>/*_final_results.html: Summary file with reference coverage stats and contigs for visualization.*_final_results.tab: Summary file with reference coverage stats and contigs.images/<SAMPLE>_<REF_NAME>.png: PNG file with the visualization of the alignment between the viral assembly and the reference viral genome.logs/: Log files.
NB: The value of <ASSEMBLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --assemblers parameter (Default: ‘spades’).
PlasmidID was used to graphically represent the alignment of the reference genome relative to a given assembly. This helps to visualize the coverage of the reference genome in the assembly. To find more information about the output files refer to the documentation.
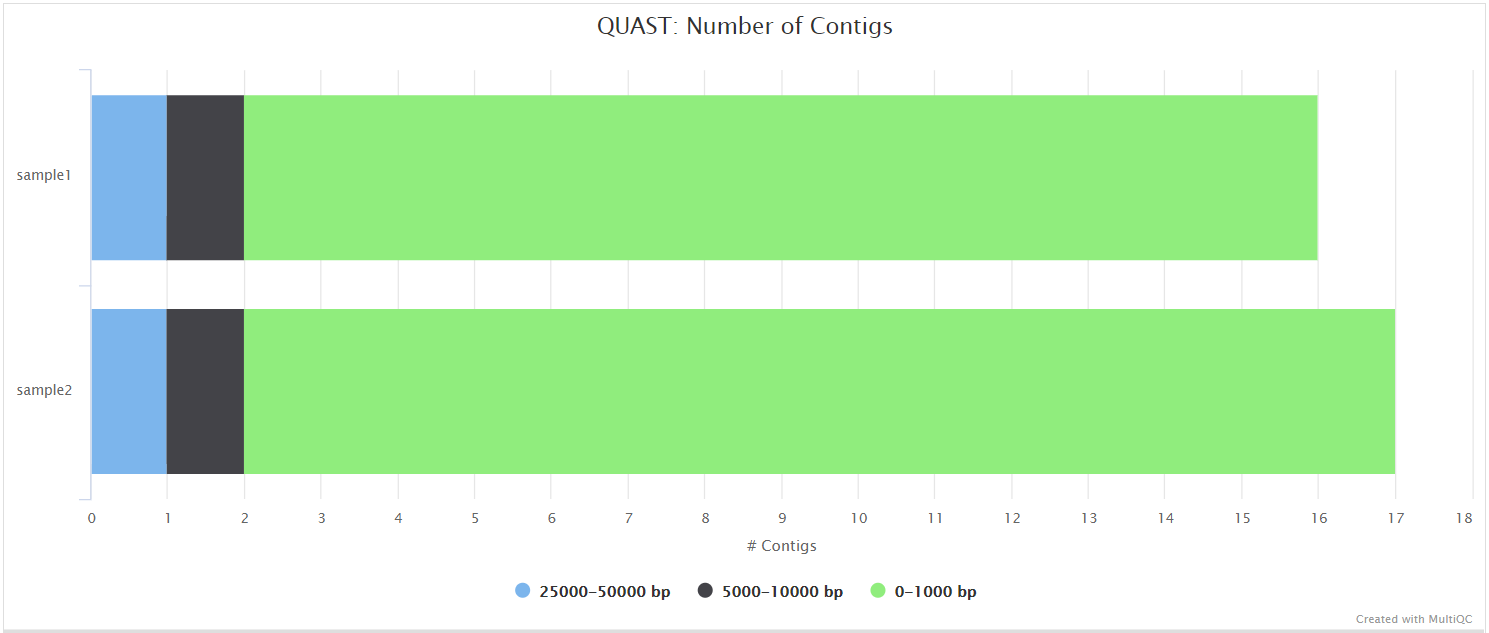
Assembly QUAST
Output files
assembly/<ASSEMBLER>/quast/report.html: Results report in HTML format. Also available in various other file formats i.e.report.pdf,report.tex,report.tsvandreport.txt.
NB: The value of <ASSEMBLER> in the output directory name above is determined by the --assemblers parameter (Default: ‘spades’).
QUAST is used to generate a single report with which to evaluate the quality of the de novo assemblies across all of the samples provided to the pipeline. The HTML results can be opened within any browser (we recommend using Google Chrome). Please see the QUAST output docs for more detailed information regarding the output files.
Illumina: Workflow reporting and genomes
MultiQC
Output files
multiqc/multiqc_report.html: a standalone HTML file that can be viewed in your web browser.multiqc_data/: directory containing parsed statistics from the different tools used in the pipeline.summary_variants_metrics_mqc.csv: file containing a selection of read alignment and variant calling metrics. The same metrics will also be added to the top of the MultiQC report.summary_assembly_metrics_mqc.csv: file containing a selection of read alignment and de novo assembly related metrics. The same metrics will also be added to the top of the MultiQC report.
MultiQC is a visualization tool that generates a single HTML report summarizing all samples in your project. Most of the pipeline QC results are visualised in the report and further statistics are available in the report data directory.
Results generated by MultiQC collate pipeline QC from FastQC, fastp, Cutadapt, Bowtie 2, Kraken 2, samtools, picard CollectMultipleMetrics, BCFTools, SnpEff and QUAST.
The default multiqc config file has been written in a way in which to structure these QC metrics to make them more interpretable in the final report.
The pipeline has special steps which also allow the software versions to be reported in the MultiQC output for future traceability. For more information about how to use MultiQC reports, see http://multiqc.info.
An example MultiQC report generated from a full-sized dataset can be viewed on the nf-core website.
Reference genome files
Output files
genome/- Unzipped genome fasta file for viral genome
- Unzipped genome annotation GFF file for viral genome
genome/index/bowtie2/: Bowtie 2 index for viral genome.
genome/db/blast_db/: BLAST database for viral genome.kraken2_db/: Kraken 2 database for host genome.snpeff_db/: SnpEff database for viral genome.snpeff.config: SnpEff config file for viral genome.
A number of genome-specific files are generated by the pipeline because they are required for the downstream processing of the results. If the --save_reference parameter is provided then the Bowtie 2 alignment indices, BLAST and Kraken 2 databases downloaded/generated by the pipeline will be saved in the genome/ directory. It is recommended to use the --save_reference parameter if you are using the pipeline to build a Kraken 2 database for the host genome. This can be quite a time-consuming process and it permits their reuse for future runs of the pipeline or for other purposes.
Pipeline information
Output files
pipeline_info/- Reports generated by Nextflow:
execution_report.html,execution_timeline.html,execution_trace.txtandpipeline_dag.dot/pipeline_dag.svg. - Reports generated by the pipeline:
pipeline_report.html,pipeline_report.txtandsoftware_versions.csv. - Reformatted samplesheet files used as input to the pipeline:
samplesheet.valid.csv. - Documentation for interpretation of results in HTML format:
results_description.html.
- Reports generated by Nextflow:
Nextflow provides excellent functionality for generating various reports relevant to the running and execution of the pipeline. This will allow you to troubleshoot errors with the running of the pipeline, and also provide you with other information such as launch commands, run times and resource usage.